
A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence
The story of Artificial Intelligence begins long before the 21st century. While the term “AI” was officially coined in the 1950s, the dream of creating intelligent machines goes back centuries.
1. The Early Ideas (Before 1950s)
Philosophers and mathematicians, like Aristotle and Alan Turing, laid the foundation for logical reasoning and computation. In 1936, Turing proposed the concept of a universal machine (now called the Turing Machine), which could simulate any process of mathematical deduction.
2. The Birth of AI (1950s–1960s)
In 1956, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was officially introduced at the Dartmouth Conference by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others. Early AI programs could solve basic problems and play games like checkers, which sparked excitement and high expectations.
3. The First AI Winter (1970s)
Despite the hype, AI development slowed due to limited computing power and unmet promises. This led to reduced funding—a period now known as the “AI Winter.”
4. Revival and Expert Systems (1980s)
AI regained interest with the development of expert systems, which mimicked human decision-making in specific fields. Companies started investing again, especially in Japan and the U.S.
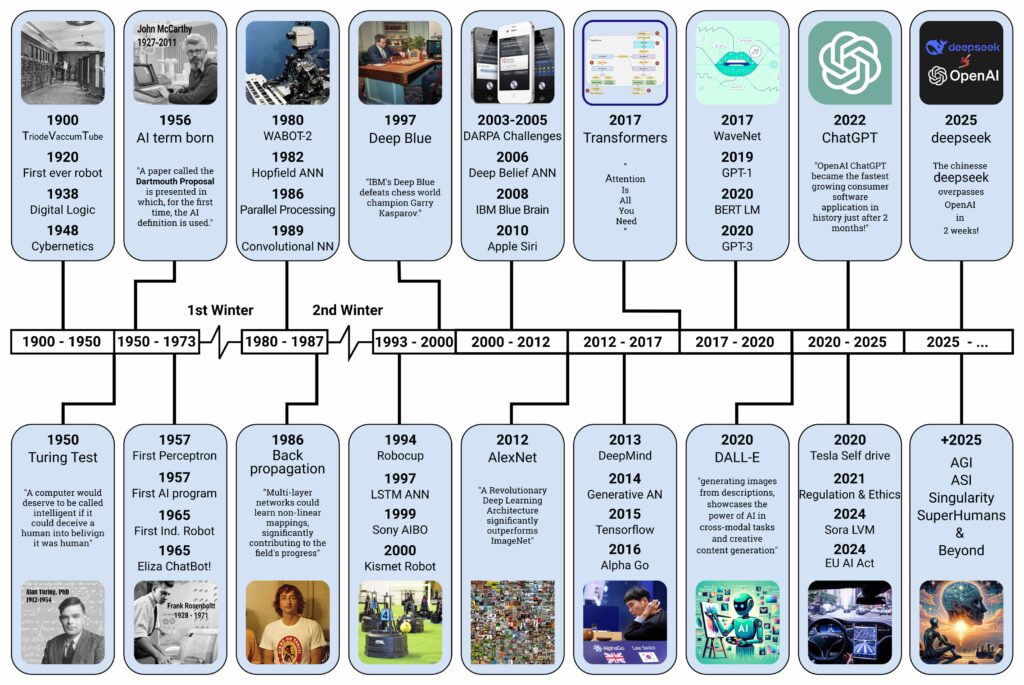
5. The Second AI Winter (1990s)
Once again, limitations in scalability and expectations led to a second AI winter. However, during this time, the groundwork for future progress was quietly being laid—especially in machine learning and neural networks.
6. Modern AI Era (2000s–2010s)
With the rise of big data, faster processors, and cloud computing, AI made a strong comeback. Technologies like speech recognition, computer vision, and autonomous vehicles became reality. In 2011, IBM’s Watson defeated human champions on Jeopardy!—a major milestone.
7. The Age of Generative AI (2020s)
The 2020s introduced a massive leap with generative AI tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and others. These models can create human-like text, images, and even code. AI is now widely used in industries ranging from finance to healthcare to entertainment.
How Was Artificial Intelligence Discovered?
Artificial Intelligence wasn’t “discovered” like a natural element—it was created by scientists, mathematicians, and engineers over time. It developed as a result of combining mathematics, computer science, logic, and psychology to simulate human thinking with machines.
Here’s how it started:
1. The Idea
The concept of intelligent machines has been around for centuries. Early philosophers imagined mechanical beings that could think. But it wasn’t until the 20th century that this idea became technically possible.
2. Alan Turing’s Vision (1930s–1950s)
British mathematician Alan Turing asked a key question: “Can machines think?” He created the theoretical basis for modern computers and introduced the Turing Test, which checks if a machine can mimic human conversation.

3. The Birth of AI (1956)
In 1956, a group of scientists met at the Dartmouth Conference in the U.S. This is considered the official birth of AI. They believed machines could simulate human intelligence and began creating programs that could solve problems, play games, and “learn.”
4. The First Programs
Early AI programs were rule-based systems that followed logical steps to make decisions. For example, programs were developed to play chess or solve math problems.
5. Growth Through Technology
As computers became faster and data became more available, AI models grew stronger. Techniques like machine learning, where machines improve by learning from data, helped AI become more powerful and useful in real-world tasks.
How Did Artificial Intelligence Get Its Name?
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first used in 1956 by American computer scientist John McCarthy, who is often called the “father of AI.”
He used the term when organizing a research project at Dartmouth College—now known as the Dartmouth Conference. The full name of the proposal was:
“A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence.”
McCarthy and his colleagues believed that “every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.”
They wanted a name that captured the goal: making machines (artificial) that could think and act intelligently—like humans. So they called it Artificial Intelligence.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is changing the world—and bringing many benefits across different industries. Here are some key advantages of AI:
1. Increases Efficiency
AI can process large amounts of data and complete tasks faster than humans. This improves productivity and reduces time in areas like customer service, data analysis, and manufacturing.
2. Reduces Human Error
Machines don’t get tired or distracted. When programmed correctly, AI can make decisions with high accuracy, helping reduce mistakes in areas like healthcare, finance, and transportation.
3. Works 24/7
Unlike humans, AI systems don’t need breaks or sleep. They can work around the clock, offering support and automation for tasks that require constant attention.
4. Supports Better Decision Making
AI can analyze complex data, find patterns, and provide insights to help people and businesses make smarter decisions—faster.
5. Enhances Customer Experience
From chatbots to personalized recommendations (like on Netflix or Amazon), AI helps companies understand customers better and offer more tailored services.
6. Automates Repetitive Tasks
AI is great at handling boring or repetitive work—like sorting emails, entering data, or monitoring security—so humans can focus on creative and strategic tasks.
7. Boosts Innovation
AI powers advanced technologies like self-driving cars, smart assistants, medical diagnostics, and even creative tools that help generate music, art, and writing.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
While AI brings many benefits, it also comes with challenges and risks. Here are some of the key disadvantages:
1. Job Displacement
One of the biggest concerns is that AI and automation can replace human jobs—especially in areas like manufacturing, customer service, and transportation—leading to unemployment in some sectors.
2. High Development Costs
Creating and maintaining AI systems can be expensive. It requires powerful hardware, large amounts of data, and skilled professionals to build and manage the technology.
3. Lack of Human Emotions and Ethics
AI can make logical decisions, but it doesn’t understand human emotions, empathy, or morality. This can be a problem in areas like healthcare or legal systems, where human judgment is important.
4. Dependence on Technology
As we rely more on AI for daily tasks, there’s a risk of becoming too dependent on machines, reducing critical thinking and problem-solving skills in people.
5. Data Privacy Concerns
AI systems often rely on huge amounts of personal data. If not handled properly, it can lead to privacy violations, data misuse, or security breaches.
6. Bias and Discrimination
AI learns from data—and if that data contains bias, the AI can make unfair or discriminatory decisions. This has been a major issue in areas like hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
7. Limited Creativity
Although AI can generate creative content, it’s still limited to patterns and data. It lacks true originality or emotional depth like a human artist or thinker.
The Role of AI in Our Daily Life
Artificial Intelligence is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s part of our everyday world. Whether we notice it or not, AI is making our lives easier, faster, and smarter. Here’s how it plays an important role in our daily routine:
1. Smartphones and Virtual Assistants
From unlocking your phone with face recognition to asking Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant for help—AI powers many of the smart features we use daily.
2. Social Media and Recommendations
AI helps platforms like Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok show you content you’re most likely to enjoy by analyzing your behavior and preferences.
3. Online Shopping
When you shop online, AI gives you personalized product suggestions, offers, and even chatbot support—making the experience smoother and more tailored.
4. Navigation and Travel
AI helps GPS apps like Google Maps and Waze to provide real-time traffic updates, suggest faster routes, and even predict arrival times.
5. Healthcare
AI assists doctors in diagnosing diseases, reading scans, and creating personalized treatment plans. Some apps even monitor your health in real-time.
6. Banking and Finance
AI detects fraud, helps with budgeting apps, and even powers virtual assistants in banking apps to help users manage their money.
7. Smart Homes
AI runs your smart home devices—from adjusting your thermostat and lights to securing your home with smart cameras and alarms.
8. Education and Learning
AI is used in online learning platforms to offer personalized lessons, track progress, and provide instant feedback to students.


Add comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.